Photo by CHUTTERSNAP on Unsplash
Cloud Computing Models : IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
A comprehensive look at cloud computing models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, including storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet. It allows businesses and individuals to access and use computing resources as needed, without having to invest in physical infrastructure or manage complex systems. Cloud computing offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility, making it an attractive option for organizations of all sizes.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides users with virtualized computing resources over the internet. This model offers a flexible infrastructure, allowing businesses to scale their resources up or down as needed.
Definition and Key Characteristics
IaaS is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It enables users to access and manage virtual machines, storage, and networking components without the need for physical infrastructure.
Key characteristics of IaaS include
on-demand provisioning
scalability
cost-effectiveness
the ability to manage resources through APIs or web-based interfaces.
Use Cases and Examples
IaaS is suitable for a variety of use cases, including:
Web hosting: Companies can host their websites on IaaS platforms, eliminating the need for dedicated servers and reducing costs.
Data storage and backup: IaaS allows organizations to store and back up their data in the cloud, providing greater flexibility and security.
Virtual desktops: Users can access virtual desktops hosted on IaaS platforms, enabling remote work and increased mobility.
Big data analysis: Organizations can leverage IaaS to process and analyze large volumes of data without investing in expensive hardware.
Development and testing: Developers can use IaaS environments to create, test, and deploy applications more efficiently.
Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and IBM Cloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is a cloud computing model that provides users with a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications. With PaaS, developers can focus on coding and application logic while leaving the underlying infrastructure management to the service provider.
Definition and Key Characteristics
PaaS is a cloud computing model that provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the need to maintain the underlying infrastructure.
Key characteristics of PaaS include
pre-built development tools
frameworks
services
scalability
automatic updates
support for multiple programming languages.
Use Cases and Examples
PaaS is suitable for various use cases, including:
Rapid application development: Developers can use PaaS to quickly build and deploy applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
Microservices architecture: PaaS platforms enable developers to create and manage microservices-based applications, increasing flexibility and scalability.
Integration and automation: PaaS solutions can help organizations integrate their applications and automate business processes.
Mobile app development: Developers can use PaaS platforms to build, test, and deploy mobile applications more efficiently.
Internet of Things (IoT) applications: PaaS provides the tools and services needed to develop and manage IoT applications.
Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service, and IBM Cloud Foundry.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a cloud computing model where software applications are provided over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications via web browsers or specialized client applications, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance.
Definition and Key Characteristics
SaaS is a cloud computing model that delivers applications over the internet, allowing users to access them through a web browser without installing or managing the software locally.
Key characteristics of SaaS include
subscription-based pricing
automatic updates
multi-tenant architecture
centralized data storage.
Use Cases and Examples
SaaS is suitable for various use cases, containing:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Salesforce is a popular SaaS CRM solution that helps businesses manage customer interactions and sales leads.
Email and collaboration: Google Workspace and Microsoft Office 365 provide SaaS solutions for email, document creation, and team collaboration.
Human Resources Management (HRM): Workday and BambooHR offer SaaS HRM solutions for employee management, benefits administration, and performance tracking.
Project management and team collaboration: Trello, Asana, and Basecamp are examples of SaaS tools for project management and team collaboration.
Accounting and finance: QuickBooks Online and Xero provide cloud-based accounting and financial management services for businesses.
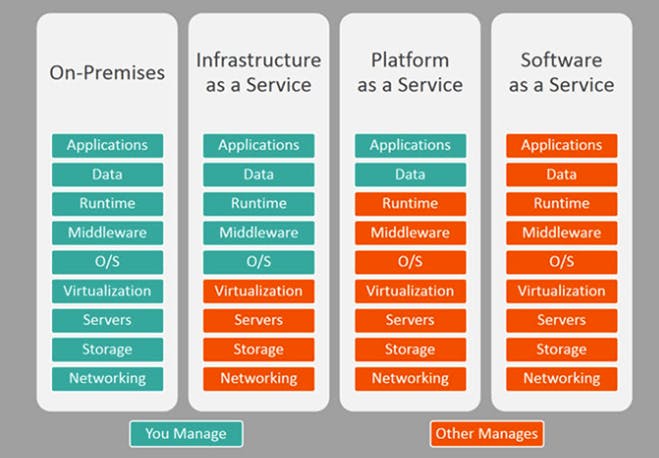
Comparison of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
While all three models fall under the umbrella of cloud computing, there are significant differences between them.
IaaS focuses on providing infrastructure resources,
PaaS provides a platform for application development, and
SaaS delivers fully developed software applications.
The level of control and responsibility varies across the models, with IaaS offering the most control and SaaS requiring the least.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations when choosing the right cloud computing model that aligns with their specific needs and goals.
Choosing the Right Cloud Computing Model
Selecting the appropriate cloud computing model depends on various factors, including the organization's requirements, budget, scalability needs, and technical expertise.
IaaS is suitable for businesses that require full control over the infrastructure, whereas
PaaS is ideal for developers looking for a managed platform to build and deploy applications.
SaaS is an excellent choice for organizations seeking ready-to-use software applications without the hassle of maintenance.
Careful consideration of these factors is essential for making an informed decision.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access and utilize computing resources. By offering scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility, cloud computing has become an indispensable tool for organizations of all sizes.
Understanding the different cloud computing models, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, is crucial for leveraging the benefits of cloud computing effectively. By selecting the right model, businesses can optimize their operations, drive innovation, and stay ahead in the fast-paced digital landscape.
