This post focuses on describing stock market indices in India.
A stock market index is a tool used to track the performance of a specific segment of the stock market. It is a statistical measure that reflects the composite value of a group of stocks that represent a particular sector, industry, or region.
Stock market indices are used by investors and financial analysts to gauge the performance of the market as a whole or to track the performance of specific sectors or companies. For example, the S&P 500 is a widely used index in the United States that tracks the performance of the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the country. Other popular indices include the Dow Jones Industrial Average, Nasdaq Composite, and Russell 2000.
Indices are typically calculated using a weighted average of the individual stock prices within the index. The weighting can be based on market capitalization, revenue, or other factors. The performance of an index is usually expressed as a percentage change from a specific time to another.
India as two benchmark indices such as [BSE Sensex] and [NSE Nifty]
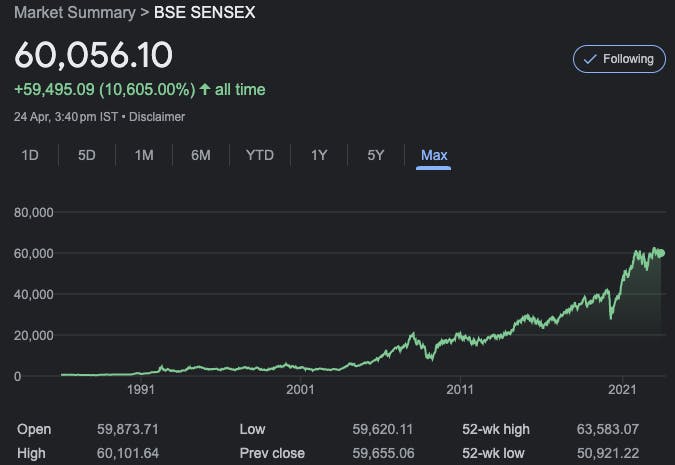
BSE Sensex
The BSE Sensex, also known as the Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitive Index, is one of the most prominent stock market indices in India. It is a benchmark index of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and tracks the performance of the top 30 companies listed on the BSE.
The BSE Sensex is calculated using a free-float market capitalization weighted methodology, which means that the weightage of each stock in the index is based on its market capitalization adjusted for the proportion of shares that are freely available for trading in the market.
The index was first introduced in 1986 and has since become a widely followed indicator of the Indian stock market's overall health and performance. The companies included in the index represent various sectors of the Indian economy, including finance, energy, technology, consumer goods, and more.
The BSE Sensex is an important tool for investors and traders to track the performance of the Indian stock market as a whole and make informed investment decisions. The index is also used by policymakers and economists to analyze the state of the Indian economy and its financial markets.
Method of Calculation
The BSE Sensex is calculated using a free-float market capitalization weighted methodology. Here's how the calculation works:
Selection of companies: The BSE Sensex includes the top 30 companies listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) in terms of market capitalization, liquidity, and other factors. The companies included in the index represent various sectors of the Indian economy.
Calculation of free-float market capitalization: The market capitalization of each company included in the index is calculated by multiplying its total outstanding shares by its current market price. However, only the shares that are available for trading in the market, or the free-float shares, are considered for the calculation. This is because some shares of a company may be held by promoters, governments, or other entities that do not actively trade them.
Calculation of index value: The BSE Sensex value is calculated by adding up the free-float market capitalization of all 30 companies included in the index and dividing it by a number called the index divisor. The index divisor is a factor used to maintain continuity and adjust for changes in the market. It is adjusted periodically to reflect changes in the market and ensure that the index remains relevant.
**Daily calculation: **The BSE Sensex is calculated and updated in real-time during trading hours. The value of the index at the beginning of each trading day is set to a base value of 100 points and changes throughout the day based on the performance of the stocks included in the index.
Overall, the BSE Sensex provides a reliable measure of the performance of the Indian stock market and is widely used by investors, traders, and policymakers to track the overall health of the market.
NSE Nifty
The NSE Nifty, also known as the Nifty 50, is a benchmark stock market index of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India. It tracks the performance of the top 50 companies listed on the NSE, which represent various sectors of the Indian economy.
The Nifty 50 is calculated using the free-float market capitalization weighted methodology, which means that the weightage of each stock in the index is based on its market capitalization adjusted for the proportion of shares that are freely available for trading in the market.
The index was introduced in 1996 and has since become a widely followed indicator of the Indian stock market's overall health and performance. The companies included in the index represent various sectors of the Indian economy, including finance, energy, technology, consumer goods, and more.
The Nifty 50 is an important tool for investors and traders to track the performance of the Indian stock market as a whole and make informed investment decisions. The index is also used by policymakers and economists to analyze the state of the Indian economy and its financial markets.
In addition to the Nifty 50, the NSE also calculates and publishes other indices, such as the Nifty Bank, Nifty Pharma, and Nifty Midcap, that track the performance of specific sectors or segments of the Indian economy.

Method of Calculation
The NSE Nifty or Nifty 50 is calculated using a free-float market capitalization weighted methodology. Here's how the calculation works:
Selection of companies: The Nifty 50 includes the top 50 companies listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India in terms of market capitalization, liquidity, and other factors. The companies included in the index represent various sectors of the Indian economy.
Calculation of free-float market capitalization: The market capitalization of each company included in the index is calculated by multiplying its total outstanding shares by its current market price. However, only the shares that are available for trading in the market, or the free-float shares, are considered for the calculation. This is because some shares of a company may be held by promoters, governments, or other entities that do not actively trade them.
Calculation of index value: The Nifty 50 value is calculated by adding up the free-float market capitalization of all 50 companies included in the index and dividing it by a number called the index divisor. The index divisor is a factor used to maintain continuity and adjust for changes in the market. It is adjusted periodically to reflect changes in the market and ensure that the index remains relevant.
Daily calculation: The Nifty 50 is calculated and updated in real-time during trading hours. The value of the index at the beginning of each trading day is set to a base value of 1000 points and changes throughout the day based on the performance of the stocks included in the index.
Overall, the Nifty 50 provides a reliable measure of the performance of the Indian stock market and is widely used by investors, traders, and policymakers to track the overall health of the market.
Some Interesting Facts about them
As per the March 2022 data, here are a few insights about the overlap between the two indices:
100% of Sensex holdings are common with Nifty50 holdings
86% of Nifty50 holdings are common with Sensex holdings
Around 31 stocks are common between the two indexes
14% of Nifty50 holdings are not part of Sensex holdings
Around 20 stocks are part of Nifty50 but not Sensex
Other Indices
There are several stock market indices in India, which track the performance of different segments of the Indian stock market. Here are some of the most commonly used stock market indices in India:
BSE Midcap: The BSE Midcap index tracks the performance of the top 100 companies listed on the BSE, which are considered to be mid-sized companies.
BSE Smallcap: The BSE Smallcap index tracks the performance of the top 500 companies listed on the BSE, which are considered to be small-sized companies.
Nifty Bank: The Nifty Bank index tracks the performance of the top 12 banking and financial services companies listed on the NSE.
Nifty Pharma: The Nifty Pharma index tracks the performance of the top 10 pharmaceutical companies listed on the NSE.
These are just a few examples of the various stock market indices in India. There are many other indices that track the performance of different sectors or segments of the Indian economy.
Summary
This post discusses stock market indices and focuses on two major benchmark indices in India: the BSE Sensex and the NSE Nifty.
A stock market index is a statistical measure that reflects the composite value of a group of stocks that represent a particular sector, industry, or region. Stock market indices are used by investors and financial analysts to gauge the performance of the market as a whole or to track the performance of specific sectors or companies.
The BSE Sensex and NSE Nifty are both calculated using the free-float market capitalization weighted methodology, which means that the weightage of each stock in the index is based on its market capitalization adjusted for the proportion of shares that are freely available for trading in the market.
Overall, these indices provide a reliable measure of the performance of the Indian stock market and are widely used by investors, traders, and policymakers to track the overall health of the market.

